Subdural hematoma: What you need to know
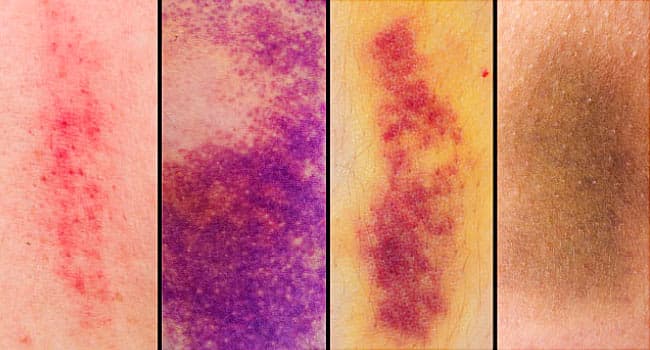
An individual with a head injury requires hematoma quick clinical consideration. Albeit an individual may not at first feel as though a lot is off-base, draining can happen inside the skull. Inward draining can prompt genuine results, including cerebrum harm and demise.
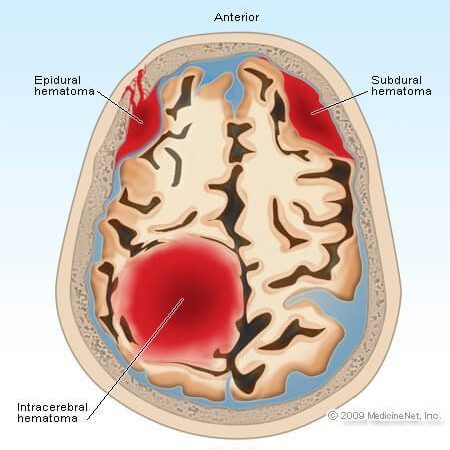
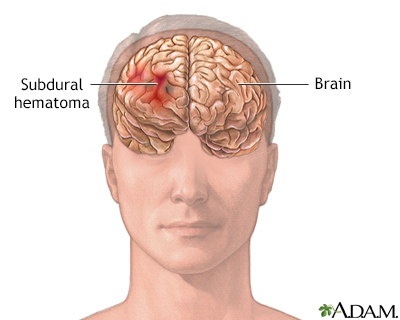
One kind of inner draining in the skull is called subdural hematoma. Individuals ought to know about the signs and side effects of head injury and look for treatment quickly if they or somebody around them experience a head injury.
What is a subdural hematoma?
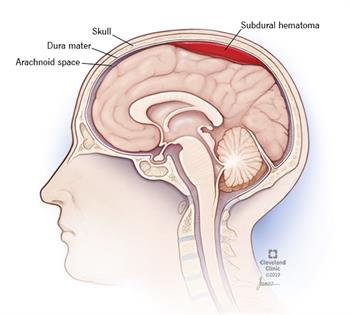
A subdural hematoma happens when a vein situated underneath the skull bursts and begins to drain. The blood gathers between the cerebrum and the skull. As this space loads up with blood, the expanding pressure causes a portion of the manifestations of subdural hematoma.
Subdural hematoma draining happens in one of the layers of tissue between the mind and the skull called the meninges. The peripheral layer is known as the dura.
If pressure keeps on working against the cerebrum, a subdural hematoma might prompt long haul medical issues or hazardous circumstances. In the most pessimistic scenario situations, untreated subdural hematomas can prompt obviousness or passing.
Subdural hematomas are a consequence of injury to the head. The seriousness of the injury decides how the subdural hematoma will be arranged.
There are two sorts of subdural hematomas: intense and ongoing.
Intense subdural hematoma
A subdural hematoma brought about by an extreme head injury is viewed as intense. Logical causes might incorporate auto crashes or a tumble from a tallness.
Instances of intense subdural hematoma are frequently harder to treat and bound to prompt long haul outcomes or demise. The danger of death from an intense subdural hematoma is in excess of 50%.
Ongoing subdural hematoma
Ongoing instances of subdural hematoma are either because of rehashed or gentle head wounds.
More established grown-ups are bound to foster persistent subdural hematoma because of expanded recurrence of falls.
More established grown-ups are additionally at higher danger on the grounds that an individual’s cerebrum recoils as they age, and this shrinkage causes the little veins on the outer layer of the mind to extend, making them more helpless against tearing
While persistent subdural hematomas are more straightforward to treat, there is as yet the danger of death or long haul wellbeing results.
Side effects
The side effects of subdural hematoma can change from one individual to another. Normal manifestations include:
- serious migraine
- change in disposition or conduct
- seizures
- slurred discourse
- loss of cognizance or dropping
- lack of care
- shortcoming
- vision issues
- unsteadiness
- retching
- disarray
Manifestations of an intense subdural hematoma happen rapidly following the injury. In instances of persistent subdural hematoma, side effects are bound to grow gradually or may not create by any means.
The manifestations happen at various rates because of the speed at which blood begins to pool and come down on the cerebrum.
In instances of ongoing subdural hematoma, little veins on the external surface of the mind might tear. The tears cause draining in the subdural layer of tissue. In these cases, indications may not show up for a long time or even weeks.
Different elements might impact an individual’s side effects. An individual’s age or other ailments both assume a part in how rapidly side effects begin to create.
Causes
The most well-known reason for a subdural hematoma is an extreme physical issue to the head. Minor head wounds are a more uncommon reason and more commonplace in more seasoned individuals.
Now and again, subdural hematomas might happen unexpectedly because of another ailment.
Hazard factors that expansion an individual’s odds of creating subdural hematoma include:
- blood thinners, like warfarin or ibuprofen
- ailments that cause blood thickening issues
- long haul liquor use or misuse
- rehashed head wounds, for example, from falls or sports
- extremely youthful or exceptionally advanced age
Finding
Analyze instances of intense subdural hematoma rapidly so therapy can start right away. Fast treatment might limit the danger of death or long haul impacts.
Instances of constant subdural hematoma might be more hard to analyze, as manifestations don’t grow quickly or might not have a conspicuous reason.
To analyze subdural hematoma, a specialist will generally utilize figured tomography (CT), or attractive reverberation imaging (MRI) outputs to get an unmistakable image of the cerebrum. The specialist will look at the sweep for indications of dying.
If the specialist distinguishes dying, they will decide the wellspring of the draining and foster a game plan to resolve the issue.
The specialist may likewise check an individual’s pulse and pulse, just as request blood work to get platelet and platelet counts. These screenings and tests are intended to search for inside draining and blood misfortune.
Treatment
An individual with a subdural hematoma will normally require a medical procedure. For intense cases, the individual will probably go through a craniotomy.
During this method, a specialist first eliminates a piece of the individual’s skull close to the site of the subdural hematoma. The specialist will then, at that point, eliminate the coagulation and will then, at that point, use pull and water system strategies to eliminate any spilled blood.
A craniotomy is a dangerous system. In certain conditions, nonetheless, it important to save an individual’s life.
For ongoing subdural hematomas or when an intense hematoma is more modest than 1 cm in width, a specialist might utilize burr opening a medical procedure. During this methodology, the specialist penetrates a little opening into the individual’s skull and additions an elastic cylinder to deplete the blood.
After medical procedure, a specialist will as a rule endorse hostile to seizure drug. An individual might have to consume the medications for quite some time or a long time. Taking these prescriptions can assist with forestalling a seizure that could cause another subdural hematoma.
Specialists normally endorse drugs to assist with diminishing enlarging around the cerebrum, which might help forestall or lessen strain in the skull soon after medical procedure.
Recuperation
Recuperation times shift significantly between people. The speed of recuperation regularly relies upon the degree of harm the subdural hematoma has caused to the cerebrum.
Just somewhere in the range of 20 and 30 percent of individuals can hope to see a full or almost full recuperation of cerebrum working.
Frequently, individuals treated rapidly have the best possibilities of full recuperation. More youthful individuals and individuals whose enlarging is controlled are bound to see better outcomes during recuperation.
Standpoint
Indeed, even after treatment, a subdural hematoma can possibly prompt demise or super durable mind harm. A fast clinical reaction and care are fundamental for allow an individual the best opportunity of endurance and full recuperation.
It is fundamental for an individual to follow all suggestions for present a medical procedure therapy on increment the odds of a good result.