Juvenile Recurrent Parotitis
What is adolescent intermittent parotitis?
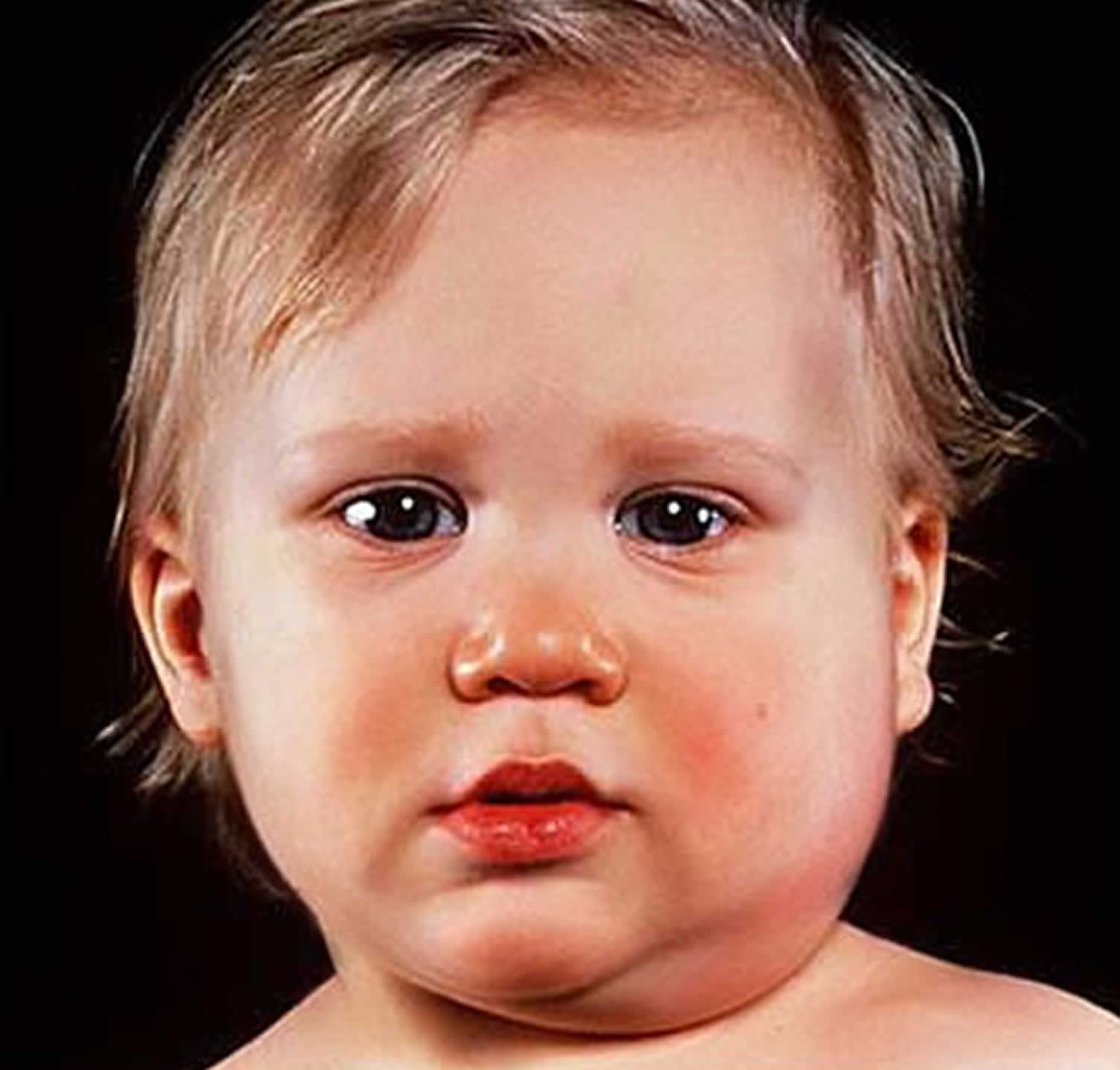
Parotitis is the expanding of one or both parotid organs, the salivary organs that are situated in the cheek between the ear and jaw on each side of the head.
Adolescent intermittent parotitis is described by repetitive scenes of parotid organ expanding.
A youngster with adolescent intermittent parotitis might have numerous scenes of expanding over a time of years, regularly joined by fever and agony or uneasiness. The condition most ordinarily starts between the ages of 3 to 6, yet can begin prior or later. As a rule, the scenes end between the ages of 10 to 15, with no further side effects.
A few kids have gentle and rare scenes. Others have scenes that are successive and exceptional to the point that they much of the time miss school.
Reasons for adolescent repetitive parotitis
The reasons for adolescent repetitive parotitis are not completely perceived. Conceivable outcomes investigated by analysts incorporate an underproduction of salivation, intrinsic mutation of the salivary channels, history of bacterial or viral contaminations, hereditary inclination, or hidden immune system problem. The component causing the enlarging of the parotic organs seems to include disturbance of the ordinary progression of salivation, prompting disease of the parotid organs.
The way that the condition normally vanishes at around the time of pubescence proposes that limiting of the salivary pipes might assume a part in causing the condition. As the kid develops, so do the channels, and the progression of spit gets back to business as usual.
- Manifestations of adolescent repetitive parotitis
- Manifestations of adolescent repetitive parotitis include:
- irritation of the parotid organ, discernible as expanding of the jaw close to the ear
- torment
- redness in the impacted space of the jaw
- fever
- repeat of irritation and enlarging in rehashed scenes, with recurrence going from once every year to 20 times each year
Every scene ordinarily endures two to seven days, however may keep going up to half a month.
The enlarging typically shows up on only one side of the head, however it can happen on the two sides.
Conclusion of adolescent repetitive parotitis
At the point when a kid has numerous scenes of enlarging and torment in one or the two jaws, the youngster ought to be seen by an ear, nose and throat subject matter expert (otolaryngologist). At Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, youngsters are found in the Head and Neck Disorders Program.
In the event that, in light of the youngster’s side effects and clinical history, adolescent intermittent parotitis is suspected, imaging studies and tests might be requested to help the finding. Care is taken to recognize conditions that can have comparative side effects, for example, salivary channel stones (sialoliths), salivary organ growths, immune system infection or lymphoma. In many cases, a meeting with a Rheumatologist is mentioned to assess for immune system illness that might introduce comparatively.
Imaging studies might include:
- a ultrasound of the jaw and neck, which uses sound waves to make pictures of within the body
- a CT filter, which utilizes a blend of X-beams to take nitty gritty photos of within the body
- a MRI, which utilizes solid magnets and radiofrequency waves to create pictures of the body
Different tests might include:
- delicately pushing on the skin over the parotid organ to decide delicacy of the space
- kneading the organ to communicate salivation for assessment
- bacterial culture of the kid’s salivation
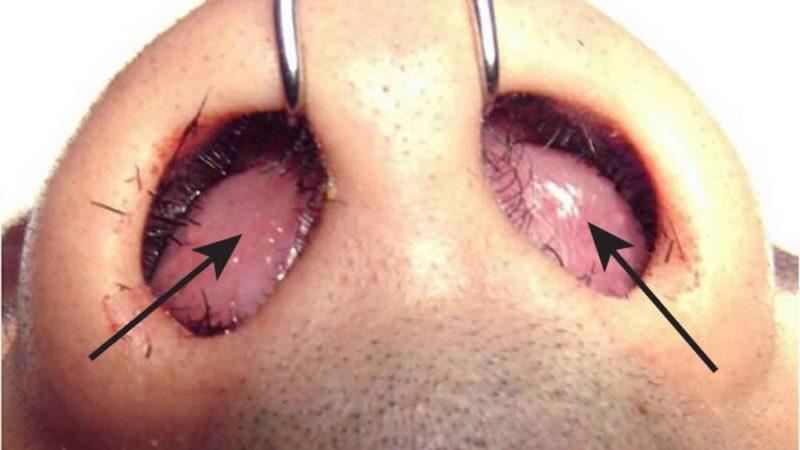
- Sialoendoscopy (examining the spit conduit with a small camera) to outwardly evaluate the salivation pipe for proof of the condition
- extraction of tissue tests for assessment under a magnifying lens
Treatment of adolescent intermittent parotitis
In most youngsters — generally 90% — the side effects of adolescent intermittent parotitis vanish in pubescence without the requirement for intrusive treatment. Along these lines, specialists are moderate in their way to deal with treatment. It is just in serious cases that intrusive medicines are thought of.
The Head and Neck Disorders Program offers master analysis and treatment for kids with adolescent intermittent parotitis. The program’s specialists have the information and experience to perceive that most patients do well with noninvasive medicines, and the ability to perform fragile methods when careful intercession is required.
Noninvasive medicines used to diminish uneasiness and decrease contamination include:
- over-the-counter torment drug (particularly Tylenol)
- cautious oral cleanliness
- back rub of the parotid organ
- utilization of hotness to the impacted region
- biting gum or sucking on harsh candy to animate the progression of spit
- keeping up with great hydration by drinking a lot of fluids
- drugs that animate the progression of spit (sialagogues)
- anti-microbials
At the point when the power and recurrence of the expanding scenes are extreme, disturbing a kid’s school and public activity and raising the danger of critical medical issues, more forceful therapy might be thought of. These might include:
- sialoendoscopy
- careful expulsion of the parotid organ (parotidectomy)
Sialoendoscopy is a technique acted in the working room where a little fiberoptic camera is utilized to peer inside the spit channel. For adolescent intermittent parotitis, the presence of within the pipes can affirm the finding. Inundating or washing out the channels with saline arrangement during sialoendoscopy or utilizing a little inflatable to broaden the pipe is one of the medicines utilized for extreme instances of adolescent repetitive parotitis. These intercessions help to return spit stream to typical and forestall repetitive scenes of parotitis. Here and there, steroids can likewise be regulated utilizing the endoscope.
Medical procedure to eliminate the parotid organ is possibly viewed as when a youngster encounters serious indications that don’t react to sialoendoscopy. The medical procedure should be performed with outrageous consideration, as the facial nerve goes through the parotid organ and should be safeguarded while the organ around it is eliminated. The facial nerve controls the capacity to close the eyes, cause a stir and grin. An enlarged or aggravated parotid organ makes this medical procedure more troublesome. To secure the facial nerve, the medical procedure might include eliminating just the upper part of the parotid organ (shallow parotidectomy).
Viewpoint for kids with adolescent repetitive parotitis
Kids with adolescent repetitive parotitis quite often face a positive long haul viewpoint. The condition can ordinarily be overseen during adolescence with noninvasive medicines that address the side effects and cleanliness rehearses that diminish the danger of contamination and ensure the teeth. In the incredible larger part of cases, the condition settle precipitously in the years around pubescence.
Indeed, even in more extreme cases, where more intrusive treatment is required, long haul results are by and large sure.